- Säker onlineshopping
- Snabba leveranser
- Hög produktkvalitet
- Vårdpersonal? Klicka här
Ryggsmärta


Kategorier
No matter whether the cause is a pinched sciatic nerve, lumbago, a slipped disc or muscular tension, back pain can be truly incapacitating.
What can you do about back pain?
Back pain accounts for the highest number of days off sick and is the number one health complaint in the UK.
In most cases, overworked muscles and ligaments or an overloaded spine is the cause. The good news: back problems often disappear spontaneously within three months. But sometimes we can also help recovery along a little – with physiotherapy or supports, for example. They feel really good and help the back to recuperate. You are fit again more quickly and can resume your normal day-to-day activities.
Vad orsakar ryggsmärta och vem drabbas?
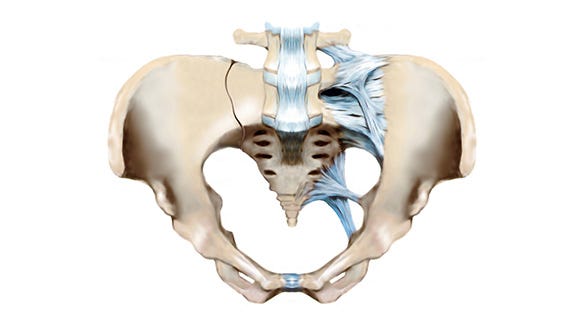
Ryggsmärtor hör till de vanligaste utbredda åkommorna och drabbar män och kvinnor i alla åldrar. Ryggraden är en av de bärande konstruktionerna i människokroppen. Den består av 24 ryggkotor, som är förbundna med diskar som gör det möjligt för dem att flytta sig i förhållande till varandra. Korsbenet och slutligen coccyxen bildar ryggradens ände.
Smärta kan utvecklas i någon eller i alla tre delarna av ryggraden – halsryggen (nacken), bröstryggen och ländryggen. Ryggsmärta orsakas av sjukdomar eller skador på diskarna (till exempel diskbråck) eller lederna mellan ryggkotorna (till exempel slitage, så kallad ”artros i facettlederna”) eller av andra omständigheter. Ryggsmärta har under de senaste åren och årtiondena utvecklats till den mest utbredda åkomman. Dr Holger Eggers, specialist för ortopedi/olycksfallskirurgi på MedCenter i Bayreuth, talar om ämnet ryggsmärta och förklarar behovet av medicinsk behandling om smärtan inte försvinner.
The spinal column
While the dorsal spine is rarely affected, about one third of all cases of spinal pain affect the cervical spine. Around two thirds of the patients have symptoms in the lumbar spine – this is known as "low back pain" or often colloquially as lumbago.
This lower section of the spine is more exposed to heavy stresses than anywhere else, among other things due to the fact that we walk upright or lift heavy objects with our backs bent.
"Acute" back pain usually lasts for up to six weeks. If it continues beyond this period for up to 12 weeks it is called "subacute", while back pain that still persists after 12 weeks is called "chronic back pain".
Typer av ryggsmärta
”Akut” ryggsmärta varar normalt upp till sex veckor. Om den fortsätter längre än denna period och upp till 12 veckor kallas smärtan ”subakut”. Långvariga ryggsmärtor (längre än 12 veckor) betecknas som ”kroniska ryggsmärtor”.
Beroende på om otvetydiga fysiska orsaker och diagnoser föreligger eller om det inte finns några tydliga igenkännliga orsaker skiljer vi mellan
Beroende på om otvetydiga fysiska orsaker och diagnoser föreligger eller om det inte finns några tydliga igenkännliga orsaker skiljer vi mellan
- icke-specifik ryggsmärta och
- specifik ryggsmärta
Dr Holger Eggers, specialist för ortopedi/olycksfallskirurgi på MedCenter i Bayreuth, talar om specifik, icke-specifik och kronisk ryggsmärta.
Non-specific and specific back pain
Icke-specifik ryggsmärta
De flesta fall kan tilldelas kategorin icke-specifik ryggsmärta. Här kan den exakta orsaken till smärtan inte diagnostiseras.
Dr Holger Eggers, specialist för ortopedi/olycksfallskirurgi på MedCenter i Bayreuth, förklarar effekterna på människans rygg på grund av hållningsproblem och för lite fysisk träning.
Specifik ryggsmärta
Om den exakta orsaken till smärtan är känd talar vi om ”specifik ryggsmärta”.
Denna orsakas exempelvis av skador, intervertebral diskdegeneration, inflammation eller slitage av lederna mellan ryggkotorna (så kallad ”artros i facettlederna”).
Symptom och åkommor
Nästan alla har upplevt ett ”stick" eller en lättare smärta i ryggen. ”Det är ryggen igen” är något vi ofta hör och våra ryggar utsätts för mycket stress varje dag. Många timmars sittande på kontoret, hopsjunken hållning framför datorn, tunga lyft och bärande eller nedböjd ställning vid arbete i trädgården: lite ryggsmärta är en del av det dagliga livet.
Om respektive symptom varar längre, bör det tas på allvar. Gör vissa rörelser ont? Strålar smärtan ut i armarna eller benen, drabbas du av domningar? Medan till exempel diskbråck kan orsaka stark smärta som strålar ut i ett ben, känns slitage på lederna mellan ryggkotorna mer som en molande och djup ryggsmärta. Smärtans exakta allvarlighetsgrad och intensitet varierar från patient till patient och beror på om han/hon har en akut skada, muskulära besvär eller slitage på ryggraden. Beroende på den kliniska bilden kan till och med andningen göra ont, till exempel när bröstryggen har drabbats, medan huvudvärk och yrsel kan orsakas av smärta i halsryggen.
Om symptom inte försvinner eller återvänder, bör man konsultera en läkare och beskriva smärtan. Läkaren kommer att informera dig om möjliga behandlingar som finns tillgängliga för dina ryggsmärtor: dessa behandlingsalternativ kan vara användning av stöd, intagande av läkemedel eller fysioterapi eller till och med en operation. En väsentlig del av behandlingen är regelbunden träning: den stärker musklerna, stabiliserar ryggraden och förebygger smärta.
De vanligaste orsakerna till ryggsmärta
Ryggraden är ett komplext system som består av kotkroppar, diskar, muskler och ledband.* Smärta uppkommer när samspelet mellan dessa strukturer störs. Vanliga orsaker är:
Diskbråck
Diskarna är placerade mellan kotkropparna: de fungerar som stötdämpare, klarar stor spänning och kompressionsbelastningar och de förhindrar att kotkropparna gnids mot varandra. Om skivans elasticitet avtar kan den yttre fibrösa ringen rivas sönder. Den geléartade kärnan kommer då att falla fram från diskens insida och orsaka ett diskbråck.
Om framfallet trycker på en nervrot, kan detta orsaka smärta i armen eller benet förknippat med onormala känslor som stift-och-nålar eller domningar. Ett framfall kan till och med resultera i muskelförlamning.
Låsning
Dålig hållning eller tung lyftning kan också förskjuta intervertebral vävnad. Detta leder till felaktig hållning och funktionella störningar i ländryggen – även kallad ”låsning”. Detta kan också påverka lederna mellan ryggkotorna. En av konsekvenserna av detta är att den omgivande muskulaturen dras samman krampaktigt och patienten intar en skyddande hållning för att lindra smärtan. Denna skyddande hållning utsätter i sin tur andra delar av ryggen för stress och smärtan kan sprida sig.
Degenerativa förändringar
När vi blir äldre påverkas våra ryggrader av förändringar på grund av slitage (så kallade ”degenerativa förändringar”), till exempel artros. Degenerativ innebär att följderna av detta slitage är irreversibla, även om många svarar väl på behandling, exempelvis genom användning av medicinsk utrustning.
Slitage på diskarna leder till att ledytorna mellan ryggkotorna gnids hårdare mot varandra. Denna överbelastning leder till leddegeneration, som kallas artros i facettlederna, om denna påverkar lederna mellan kotkropparna (facettleder).
Muskulära orsaker
Ländryggen stabiliseras av musklerna. Här spelar musklerna över magens framsida och sidor också en viktig roll. En stabil bålmuskulatur lindrar stressen på diskarna och facettlederna och skyddar ländryggen mot överbelastning. Ryggsmärta kan utvecklas om musklerna är svaga eller har utvecklats asymmetriskt. Enskilda muskler kan överbelastas, bli hårda eller till och med förkortas.
Detta orsakas av dålig hållning, för lite träning, ensidig idrott eller till och med stress.
Deformationer
Orsaken till ryggsmärta kan emellertid ligga någon helt annanstans, till exempel i fötterna. Våra fötter bär oss bokstavligen genom dagen och belastas med hela vår kroppsvikt. Detta utsätter dem för enorma påfrestningar. En felaktig fotarkitektur kan därför också vara en orsak till ryggsmärta. Även benlängdsskillnader kan leda till snedhet i bäckenet och slutligen till ryggsmärta.
De goda nyheterna: Många ryggproblem löser sig själva på endast några veckor. Icke-specifika ryggsmärtor åtgärdas huvudsakligen med hjälp av mobiliseringsbehandling och, efter samråd med en läkare, genom intag av läkemedel. Även övningar för att stärka muskulaturen kan vara lämpliga, till exempel medis ryggövningar.
Stress leder till ryggsmärta




Huvudsakligen stillasittande yrken och brist på fysisk träning i vardagen kan orsaka att muskelspänningar och ryggsmärtor utvecklas trots att själva ryggraden är frisk.
Visste du att psykisk spänning såsom stress på jobbet eller i våra privatliv gör att kroppen blir spänd? Läs vår vitbok för att ta reda på mer om orsakerna till ryggsmärta och påverkan av stress på ryggens hälsa.
Förebyggande – tips för stark rygg
Vi kan alla avlasta våra ryggar i vardagen och avvärja smärta.
Övningar som gynnar din rygg.
Det finns övningar för att stärka ryggen som lätt kan integreras i ditt dagliga liv. Tillsammans med en fysioterapeut har vi sammanställt några exempel på övningar till dig.
Testa dem – din rygg kommer att tacka dig!
- Träna regelbundet: även endast tre moderata träningspass på vardera 45 minuter i veckan kan öka vårt välbefinnande, stödja immunförsvaret och hålla oss i form. Skonsamma idrotter såsom simning eller power walking är särskilt snälla mot våra leder.
- Hälsosam kost: en balanserad kost håller oss i form och hjälper oss att minska övervikt och belastningen på ryggen.
- Smart lyftning: alltid när vi lyfter tunga föremål bör vi gå ner på huk och belasta våra benmuskler ”i stället för att låta ryggen lyfta”.
- Bär rätt: det är bäst att bära tunga föremål nära kroppen. Undvik ensidig belastning av en arm.
- Håll dig aktiv: alla som sitter vid ett skrivbord timme efter timme bör ta alla tillfällen i akt att röra på sig – till exempel att ta trappan istället för hissen, stå upp då och då när du ringer eller ta en promenad när det är dags för lunch.
Practical tips: Exercises to maintain a healthy back




Lower back pain is estimated to affect at least 60%-80% of the population at some time in their lives.
Here’s the good news: there are back strengthening exercises and tips that you can easily integrate into your daily life.
Our guide offers you many recommendations on how you can live your life in a more back-friendly way - by moving regularly and strengthening the back muscles. Even the simplest things can have a positive effect on your back.
Try them out - your back will love you for it!
Behandling av ryggsmärta
Ryggsmärtor kan behandlas med många olika metoder. Den läkare som behandlar dig kommer att avgöra om en konservativ behandling (utan operation) är möjlig eller om det i allvarliga fall krävs ett kirurgiskt ingrepp.



Medicinsk utrustning


Vilken medicinsk utrustning är tillgänglig och hur skiljer sig de medicintekniska produkterna för behandling av ryggsmärtor?
Läs i vår vitbok om vilken medicinsk utrustning man kan använda för att lindra långvariga och kroniska ryggsmärtor.
Fysioterapi och massage
Fysioterapi bygger på att patienten utför särskilda ryggövningar under tillsyn. Dessa kan mobilisera ryggraden, lindra spänningen och stärka bålmuskulaturen. Massage, ultraljudsbehandling eller elektroterapi kan främja läkning och lindra smärta.
Läkaren bestämmer vilka övningar som är mest lämpliga för patienten. medis fysioterapiövningar är mycket lämpliga för många patienter. Till exempel hjälper de att stärka ryggraden och lindra smärta.
Läkemedel och salvor
Läkemedel som lindrar smärta och hämmar inflammation samt salvor kan hjälpa till att lindra smärta på kort sikt. Detta förhindrar obekväm hållningskorrigering. Du bör konsultera en läkare innan du tar några tabletter.
Back pain - diagnostic investigations, prevention and treatment
Dr Holger Eggers, specialist for orthopaedics/accident surgery at the MedCenter in Bayreuth, talks about diagnostic investigations, prevention, treatment and medical devices for back pain.
Stöd och ryggortoser
Stöd och ortoser är medicinska hjälpmedel speciellt konstruerade för behandling av smärtor i muskler, senor, leder och ryggen. De anpassar sig perfekt till kroppens anatomiska förhållanden, kan lindra smärta och bidra till rörlighet. Beroende på typ av sjukdom används olika hjälpmedel. Stöd för nedre delen av ryggen kan stabilisera och avlasta ländryggen.
Mer stabila stöd, så kallade ortoser, kan räta upp ländryggen och ge mer intensivt stöd och avlastning. Dessa hjälpmedel kan kompensera fysiska begränsningar och möjliggöra större rörelsefrihet, aktivitet och bättre livskvalitet.
Produkter från medi
Ryggövningar
Starka muskler kring ryggraden skyddar den mot slitage, muskelspänningar och smärta. Ryggsmärta kan motverkas av regelbunden fysisk träning i en ryggskola, med speciella övningar för ryggraden och skonsamma idrotter som simning eller power walking.
Övningsprogrammet har utformats så att en komplett uppsättning övningar för att stärka och stretcha din rygg kan genomföras på cirka 20 minuter. Det vore perfekt om du genomför detta program två eller tre gånger i veckan. Viktigt: fråga först din läkare om någon av övningarna är olämpliga för dig.
Strengthening exercises
Head nodding
Head nodding: Exercise to strengthen the neck muscles


Starting position:
- Sit on a chair with your knees bent at about 90°.
- Lean forward with your upper body, keeping your back straight.
- Support your elbows on your thighs with your elbows bent at about 90°.
- Stretch the exercise band around the back of your head in front of your ears with modified tension.
- Hold the ends of the exercise band tightly with your left and right hands.
Exercise:
- Lift your head upwards with small movements against the tension of the exercise band.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- head and neck straight
- small movements
Shoulder pulls
Shoulder pulls: Exercise to strengthen the upper back and posterior shoulder muscles


Starting position:
- Sit on a chair with your knees bent at about 90°.
- Thread the exercise band around the handle of the closed door (or alternatively around another object at door handle height that doesn‘t give way) and grasp both ends of the exercise band firmly, holding one end in each hand.
- For a firm hold, it is best if you loop the ends of the exercise band around your wrists.
- Stretch the exercise band with reasonable tension.
- Keep your arms and the exercise band in a horizontal line.
Exercise:
- Pull your elbow horizontally backwards against the tension of the exercise band, thereby moving the strap and your arms in a straight line.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- tense your abdominal muscles!
- move the strap and your arms in a straight line
- pull your shoulder blades together (don‘t just bend your arms!)
Hip pulls
Hip pulls: Exercise to strengthen the back muscles / the large back muscle
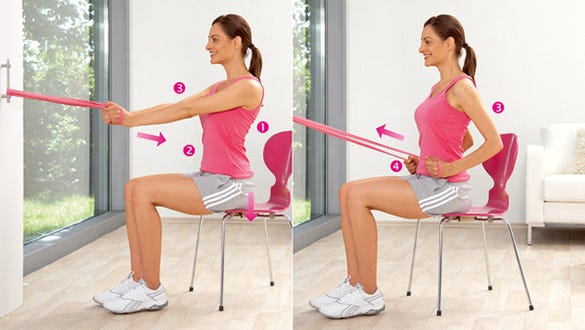

Starting position:
- Sit on a chair with your knees bent at about 90°.
- Thread the exercise band around the handle of the closed door (or alternatively around another object at door handle height that doesn‘t give way) and grasp both ends of the exercise band firmly, holding one end in each hand.
- For a firm hold, it is best if you loop the ends of the exercise band around your wrists.
- Stretch the exercise band with modified tension.
- Keep your arms straight and pointing slightly downwards.
Exercise:
- Pull your elbows horizontally backwards close to your body against the tension of the exercise band.
- Pull your hands towards your hips.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- tense your abdominal muscles!
- hold your elbows in tightly
- pull your hands towards your hips
Trunk bends
Trunk bends: Exercise to strengthen the lower back muscles


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your feet slightly apart and knees slightly bent.
- Grasp both ends of the exercise band firmly, holding one end in each hand.
- Now stand with both feet on the exercise band.
- Lean your upper body forwards with your back straight.
- Stretch the exercise band with reasonable tension.
- Keep your arms straight.
Exercise:
- Pull the exercise band vertically upwards.
- Keep your back straight and only straighten up your upper body.
- Keep your legs in the starting position, do not move them.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- tense your abdominal muscles!
- knees slightly bent
- arms held out straight
Leg raises
Leg raises: Exercise to strengthen the buttock muscles


Starting position:
- Sit on a chair with your knees bent at about 90°.
- Lean forward with your upper body, keeping your back straight.
- Support your elbows on your thighs with your elbows bent at about 90°.
- Stretch the exercise band around the back of your head in front of your ears with modified tension.
- Hold the ends of the exercise band tightly with your left and right hands.
Exercise:
- Lift your head upwards with small movements against the tension of the exercise band.
Please note:
- tense your abdominal muscles!
- do not bend your upper body forwards or backwards
- keep your knees slightly bent
Side pulls
Side pulls: Exercise to strengthen the lateral trunk muscles


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your feet apart and knees slightly bent.
- Hold both ends of the exercise band firmly in your right hand.
- Bend your upper body to the side with your back straight.
- Now stand with your right foot in the large exercise band loop.
- Stretch the exercise band with reasonable tension.
- Keep your arms straight.
Exercise:
- Pull the exercise band vertically upwards.
- Keeping your back straight, straighten your upper body and lean over to the other side.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- tense your abdominal muscles!
- neck, back and leg in a straight line
Sit-ups
Sit-ups: Exercise to strengthen the upper abdominal muscle
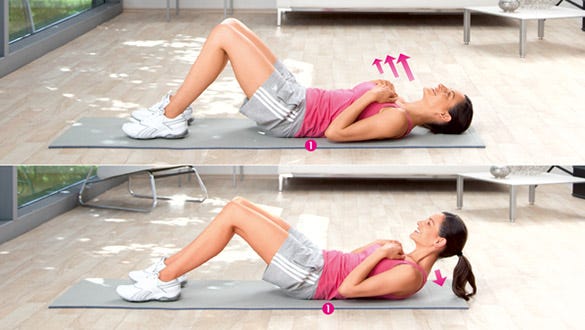

Starting position:
- Bend your knees to about 90° with your legs slightly apart.
- Press your lower back down against the floor.
- Keep your elbows by your side and your hands on your chest, not your neck.
- Rest your head on the floor.
Exercise:
- Lift your head, shoulders and chest upwards.
- Keep your lower back pressed against the floor.
Please note:
- press your lower back against the floor
Leg lifts
Leg lifts: Exercise to strengthen the lower abdominal muscles and the hip flexors


Starting position:
- Lie on your back on a firm surface.
- Bend your knees to about 90° with your legs slightly apart.
- Press your lower back down against the floor.
- Lay your arms on the floor by your body.
- Rest your head on the floor.
Exercise:
- Lift your legs up until the angle between your upper body and thighs is about 90°.
- The angle at the knee remains unchanged.
- Keep your lower back pressed against the floor.
Please note:
- press your lower back against the floor
- perhaps lay a pillow under your head
Stretching exercises
Head presses
Head presses: Exercise to stretch the neck muscles


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your feet slightly apart and knees slightly bent.
- Clasp your hands together behind your head with your elbows pointing forwards.
Exercise:
- Press your head forwards with your hands.
- Keep your back straight.
- Keep your legs in the starting position, do not move them.
- You will feel the stretch in the neck muscles.
Please note:
- back straight
- knees slightly bent
Head pulls
Head pulls: Exercise to stretch the lateral neck muscles


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your feet slightly apart and knees slightly bent.
- Pass your left or right hand over the top of your head and hold your head above the ear.
- Keep your arm on the same plane as the body.
Exercise:
- Pull your head over to the same side as the arm.
- Keep your back straight.
- Keep your legs in the starting position, do not move them.
- You will feel the stretch in the neck muscles.
- You can increase the stretch by pushing the other arm towards the floor.
Please note:
- keep your upper body upright
- with your head looking forwards
- knees slightly bent
- pull your head to the side with your hand
- push your other arm towards the floor
Shoulder pulls
Shoulder pulls: Exercise to stretch the upper back and shoulder muscles


Starting position:
- Sit on a chair with your knees bent at about 90°.
- Keep your back and head straight.
- With your left hand hold the handle of a closed door (or alternatively another object at door handle heigh that doesn‘t give way).
- Grasp the wrist of the outstretched arm with your right hand.
Exercise:
- Pull your upper back / shoulder blade backwards.
- Keep your neck relaxed.
- You will feel the stretch in your back and shoulders.
- You can increase the stretch by pushing your right hand further forwards.
Please note:
- keep your back straight
- arm stretched
- pull your upper back / shoulder blade back
Trunk pulls
Trunk pulls: Exercise to stretch the lateral trunk muscles


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your feet slightly apart and knees bent.
- Keep your back and head straight.
- With your left hand, hold a door handle of a closed door (or alternatively another object).
- Place your right hand or right forearm on your right thigh.
Exercise:
- Lean forward with your upper body.
- Keep your arm, neck and back in an almost straight line.
- Turn your pelvis slightly to the right and push your upper body slightly to the left (like leaning into a curve).
- You will feel the stretch running from your shoulder down your whole side to the pelvis.
Please note:
- straight back
- legs bent!
- arms, neck and back in an almost straight line
- pelvis turned slightly to the right and upper body pushed slightly to the left (like leaning into a curve)
Forward bending
Forward bending: Exercise to stretch the lower back muscles


Starting position:
- Sit down on a firm surface.
- Bend your legs slightly keeping your knees a little apart.
- Keep your back, neck and head straight.
- Place your hands on your knees.
Exercise:
- Now lean forwards while keeping your back straight.
- Do not bend your neck or upper back.
- Move your stretched arms towards the tips of your toes.
- You will feel the stretch in your lower back.
Please note:
- keep your back straight when leaning forward (do not bend your neck or upper back)
- legs bent
Lower body twisting
Lower body twisting: Exercise to stretch the lower and lateral back and buttock muscles


Starting position:
- Lie on your back on a firm surface.
- Straighten your right leg, bend your left leg, lay your left foot on your right knee.
- Lay your outstretched left arm on the floor, place your right hand on your left thigh.
Exercise:
- Now move the bent leg over the straight one.
- As you do so, twist your body from the chest down to the right.
- Your left arm remains the floor, your chest does not twist, your head looks in the opposite direction.
- You will feel the stretch in the lower/lateral back muscles and in your bottom.
Please note:
- arm stays on the floor
- head turns to the opposite side
Leg pulls
Leg pulls: Exercise to stretch the buttock muscles


Starting position:
- Lie on your back on a firm surface, lay your arms down next to your body.
- Press your lower back down against the floor.
- Bend your right knee to an angle of about 90°.
- Bend your left knee and lay your ankle on the right leg below the knee.
Exercise:
- Now hold your right leg below the kneecap.
- Pass your left hand between both legs and grasp it with your right hand around the right leg.
- Now pull your right calf towards your face.
- You will feel the stretch in your buttock muscles.
Please note:
- press your lower back against the floor
Hip tilt
Hip tilt: Exercise to stretch the groin region and the hip flexors


Starting position:
- Stand on a firm surface with your legs slightly apart.
- Hold your arms straight out in front of you.
Exercise:
- Keep your upper body and legs straight and tilt or push your pelvis forwards.
- You will feel the stretch in your groin.
- You can increase the stretch in your groin region by keeping your legs straight and turning your pelvis (not your upper body!) slightly further to the left or the right.
Please note:
- pelvis tilts / is pushed forwards
Fascia training
Discover the soothing effect of the specific massaging of local body regions and muscle groups. One of the aims of the myofascial release** method is to stimulate tissue circulation and thus increase tissue tone. The German Society for Osteopathic Medicine (DGOM e.V.) defines this as: all muscles are enveloped by the so-called fasciae. The fasciae themselves are connected with each other all over the body. The fasciae are stimulated by gentle pressure and tension. This improves the circulation and triggers reactions to normalise tissue tone.
Exercises you can do yourself with your BLACKROLL® MINI
You can do the exercises for myofascial release with little effort and very effectively with the BLACKROLL® MINI.
Discover the soothing effect of a specific massaging of smaller body regions and muscle groups: this relieves muscular tension and can actively support the healing process after injuries. The massage roll is so small and handy that can fit in every holdall.
Fascia training
Back
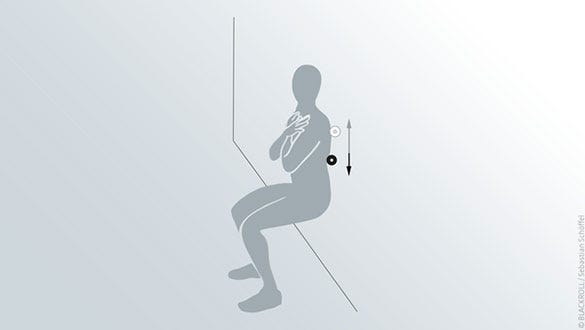

Starting position
- Stand upright
- Place the BLACKROLL® MINI between back and wall just over your hip.
Exercise
- Roll out your back in between hip and shoulder by moving up and down
- Vary with pressure by changing your balance point
Lateral trunk & latissimus
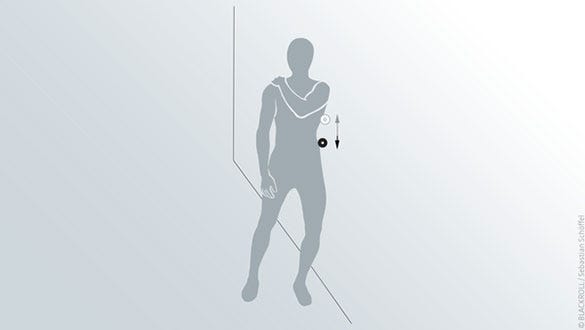

Starting position
- Stand upright
- Place one arm on the opposite shoulder
- Place the BLACKROLL® MINI between wall and thorax underneath your armpit
Exercise
- Roll out your thorax between hip and shoulder by slowly moving up and down
- Vary with pressure by working with your balance point
- When you reach the lowest point near your hip slowly get back into the initial position
- Change sides
Upper arm
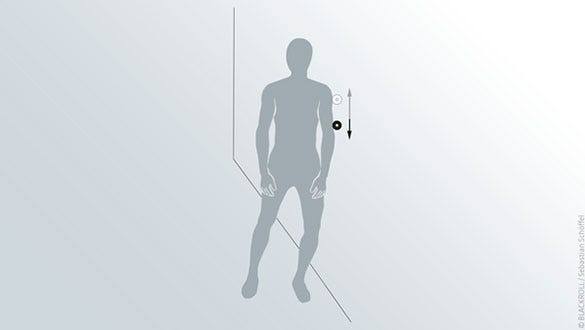

Starting position
- Stand upright
- Place the BLACKROLL® MINI between wall and upper arm near your shoulder
Exercise
- By moving up and down roll out your upper arm between elbow and shoulder
- Try changing pressure – both strength and pressure point - by working with your balance point
- When reaching the lowest point on your upper arm slowly return to the initial position
Underarms & hands
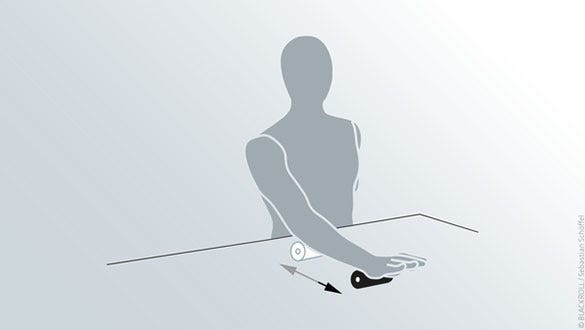

Starting position
- Sit upright at a table
- Place the BLACKROLL® MINI under your underarm close to your wrist
Exercise
- Roll out your underarm between wrist and elbow by moving back and forth on the BLACKROLL®s/sup> MINI
- When you reach your elbow slowly move back into the initial position
Plantar fascia


Starting position
- Stand upright
- Position the BLACKROLL® MINI under the sole of your foot
Exercise
- Roll back and forth with your foot on the BLACKROLL® MINI from heel to toes
- Repeat with both feet
- Apply pressure on different areas of your feet (heel, ball, right and left side) by working with your balance point on the BLACKROLL® MINI
Shin
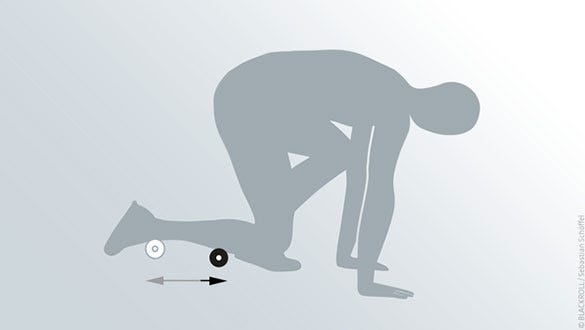

Starting position
- Get into an all-fours position
- Support yourself on your toes and lightly angled arms
- Raise your knees just a little
- Position the BLACKROLL® MINI just underneath your knee and put your right shin on it
Exercise
- Roll your shin back and forth on the BLACKROLL® MINI
- Move your leg to the left and right
- The pain should remain bearable: Choose the pressure according to this rule
- Change sides
Calf & achilles tendon
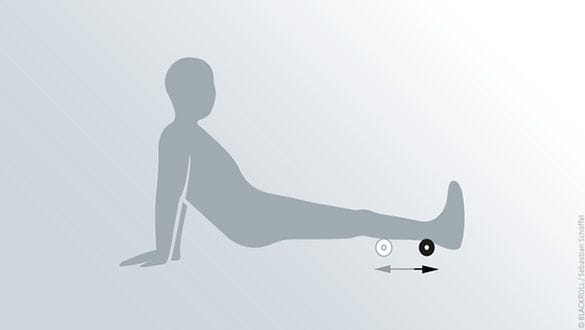

Starting position
- Sit upright on the floor supporting yourself on your hands
- Place the BLACKROLL® MINI under your right calf
- Establish your left leg next to your right knee
Exercise
- Slowly and cautiously roll out your calf
- The well established left leg helps with controlling the exercise as it supports the rolling movement and helps raising your buttocks
- To secure a full roll out of the calf slowly rotate your right leg from left to right
- Change sides
Ergonomisk arbetsplats




Ryggsmärtor börjar ofta på jobbet. Sitta i flera timmar eller med felaktig hållning kan belasta muskler, leder och orsaka smärta. Detta gäller särskilt för jobb som kräver att man ofta böjer sig, lyfter och bär tunga laster.
Give the lower back support where it is most needed with supports and braces from medi
medi's range of supports and braces offer the right medical device for many different conditions. The products convince patients because they are comfortable to wear, are made of skin-friendly and breathable materials and are available in a wide range of sizes – so everybody can find exactly the support or brace they need. Thanks to clever details such as practical hand loops or particularly soft borders, all medi’s medical devices are easy to handle and do not cut into the skin, even when worn for long periods.
Tense, sprained or strained – the lower back is particularly often affected by pain and injuries. This is where medi's supports and braces come into their own: they can stabilise the back, relieve muscular tension and ease pain on movement. The medical devices achieve these positive effects with their multidimensional mode of action. They stabilise the lumbar spine, relieve pain and enhance mobility. This can prevent further loss of muscle mass, so-called "muscle atrophy".
Guide to back treatment




Back ache often has many different causes: most people (approx. 85% of all cases) have so-called non-specific lower back pain, in which several different causes lead to back pain. These can be overstrain, contracture or dysfunction of ligaments, muscles, facet joints and intervertebral discs.
Here's how to get your back fit again: There are many simple exercises for keeping the back fit or even strengthening it. This guide describes these clearly and with many pictures. You can keep all the parts of your back fit and healthy with eight strengthening and eight stretching exercises. The guide is rounded off with a chapter on the causes of back pain and a chapter on helpful supports and braces from medi.
Elegant med en ortos – den praktiska stilguiden




Vill du veta mer om hur du kan klä dig för alla tillfällen även med en ryggortos? Vår handbok kommer att visa dig hur! Ta en titt på outfit-tipsen för en mängd olika tillfällen.
Ha kul med stil!
Mer information
* Klein, Dr Christoph (2014): Orthopaedics for patients. Understanding medicine. Remagen: Published Michels-Klein, p. 277.
** The word "myofascial" stems from "myo" for muscles and "fascial" for fasciae. Doctors define fasciae as connective tissue structures that surround our muscles and organs.